Understanding Neuropathy: The Invisible Damage to the Nervous System
What is Neuropathy?
Neuropathy is often called peripheral neuropathy. It results from damage to the peripheral nerves. These nerves send messages from the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body. When damaged, these messages can cause disruptions. This disruption can lead to many symptoms. These symptoms can range from mild discomfort to severe pain and disability.
Early Signs and Symptoms
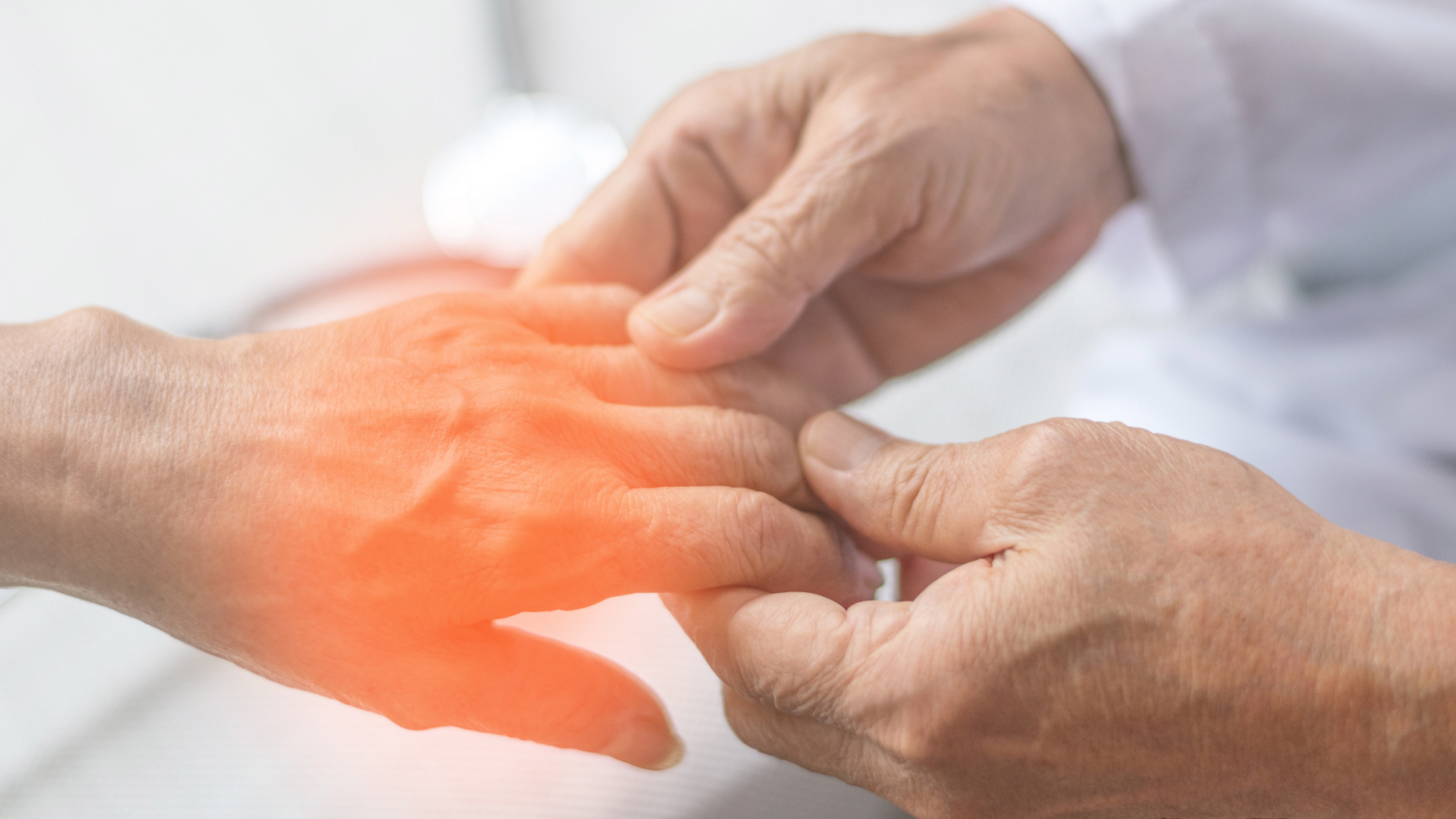
In the early stages of neuropathy, symptoms can be subtle and easy to overlook. Many people first experience a tingling or numbing sensation in their hands or feet. This tingling is often described as a "pins and needles" feeling. Another common early sign is a gradual onset of pain, which can be sharp, burning, or throbbing. Some people might notice that they're more sensitive to touch. They feel pain from stimuli that shouldn’t cause it, such as a light touch or bed sheets.
As the condition progresses, these symptoms can become more pronounced. The numbness can spread up the arms and legs, and the pain can become more intense and constant. Some people may start to feel muscle weakness. This weakness can make it hard to do everyday tasks. These tasks include walking, buttoning a shirt, and holding objects.
Progression and Late Stage Symptoms
In more advanced stages of neuropathy, the symptoms can become more debilitating. The pain may become bad and constant. The numbness can cause a complete loss of feeling in the affected areas. This is especially dangerous. It means that injuries or infections can go untreated. This can lead to more complications.
Weakness can become waste. The muscles shrink and lose strength. This can cause coordination and balance problems. They raise the risk of falls and injuries. Some people may also have autonomic symptoms. Nerve disruptions halt involuntary physical functions. These symptoms can include digestive issues. They can also cause problems with bladder control. They lead to sweating and changes in blood pressure. These problems can lead to dizziness or fainting.
Causes of Neuropathy
There are many potential causes of neuropathy. Diabetes is one of the most common, as high blood sugar levels can damage nerves over time. Other causes may include nerve injuries, infections, autoimmune diseases, certain drugs, and toxins. Sometimes, the cause of neuropathy is unknown. Doctors know this condition as idiopathic neuropathy.
Treatment Options
There is no cure for neuropathy. However, there are many treatments to manage symptoms and improve life. The first treatment step is often finding the cause of the nerve damage. If we've found it, we address it. For example, managing blood sugar helps people with diabetes. It can slow nerve damage.
Doctors use effective medications to control pain levels. These can include over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen. They can also include prescription medications such as anticonvulsants, antidepressants, and topical treatments. In some cases, doctors may prescribe stronger pain medications, including opioids. But, these drugs are a last resort due to the risk of addiction.
Physical therapy can also help. It's good for those with muscle weakness or coordination problems. Physical therapists can help develop exercise routines that improve strength, flexibility, and balance. Occupational therapists may also recommend helping people adapt their daily activities. They use assistive devices to make tasks easier.
Advances in Research
Research into neuropathy and its treatments is ongoing. There have been many promising developments. One area of focus is on nerve regeneration and repair. Scientists are exploring ways to grow new nerve fibers. They also want to repair damaged ones. This includes studying stem cells and growth factors. They could promote nerve healing.
Another area of research is the development of new medications. They can better manage neuropathic pain with fewer side effects. For example, researchers are studying drugs. The drugs target specific pathways in pain signaling. They could provide more precise pain relief.
Researchers are also exploring gene therapy as a potential treatment for neuropathy. This approach involves modifying or replacing defective genes that are causing nerve damage. Gene therapy is still experimental. However, it holds promise for treating some types of hereditary neuropathy.
Also, technological advances have led to devices that can help manage symptoms. For example, TENS devices use low-voltage electrical currents. They relieve pain. Spinal cord stimulators are devices implanted to send electrical pulses, blocking pain signals.
Dr. Dombroski has advanced electric technology that has proven applications for nerve and muscle damage. This machine is similar to a TENS machine but much more effective. If needed, he or his assistant will use this as treatment and promote healing.
Conclusion and Next Steps
Neuropathy is complex. It's often debilitating. It reshapes a person's entire existence. Finding and managing it early is crucial. They prevent symptoms from getting worse and reduce complications. There is no cure. But, drugs, therapy, and lifestyle changes can help. They can manage symptoms and improve daily functioning. Research is ongoing. It continues to offer hope for better treatments. It is bringing us closer to better outcomes for those with neuropathy.
Dr. Dombroski is a leading expert in nerve damage and healing. He has helped many patients over the years overcome or limit neuropathy, Guillain Barre Syndrome, and other nerve injuries and conditions. His state-of-the-art equipment and foremost knowledge right here in Fort Worth, TX. Give his office a call at 817-367-9289 today to set an appointment and see how he can help you or a ooved one like he has for so many others in Fort Worth, and all around the United States!