Finding Hope: Promising Advances in the Search for a Guillain-Barre Cure
In the world of medical advancements, finding a cure for rare diseases often requires perseverance, innovation, and hope. One such disease that has been the focus of intense research and investigation is Guillain-Barre Syndrome (GBS). This neurological disorder, characterized by the immune system attacking the nerves, can cause paralysis and even be life-threatening. However, recent scientific developments and breakthroughs are bringing hope to the millions of people affected by this condition.
With the growing understanding of the underlying mechanisms of GBS, researchers have made promising strides toward finding a cure. From exploring the potential of stem cells to developing new immunotherapies, these groundbreaking approaches are offering renewed optimism for patients and their families.
In this article, we delve into some current advances in the search for a Guillain-Barre cure. We'll examine the latest research findings, discuss the potential treatment options on the horizon, and highlight the impact these developments could have on improving the lives of GBS patients.
Understanding Guillain-Barre Syndrome (GBS)
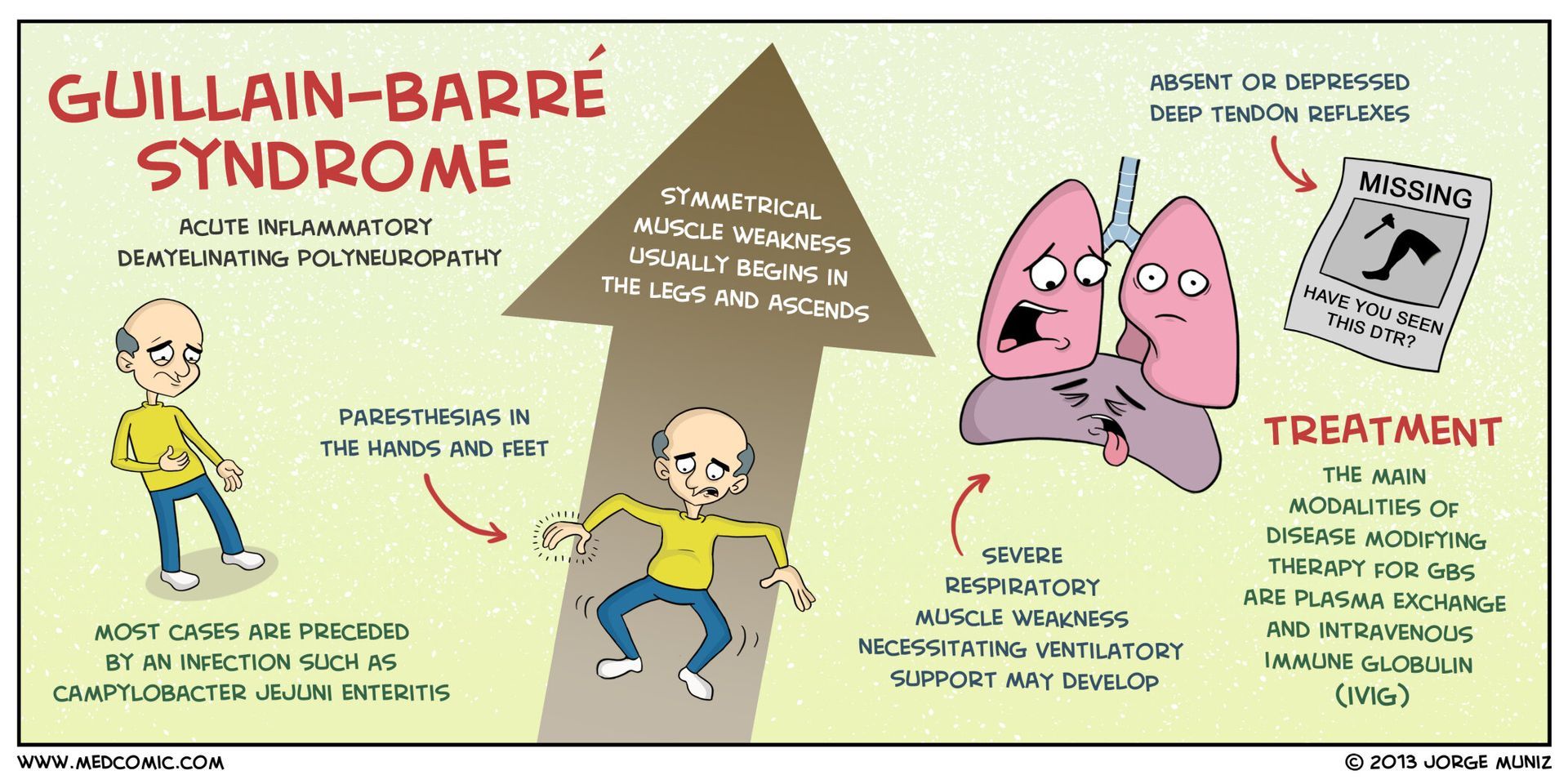
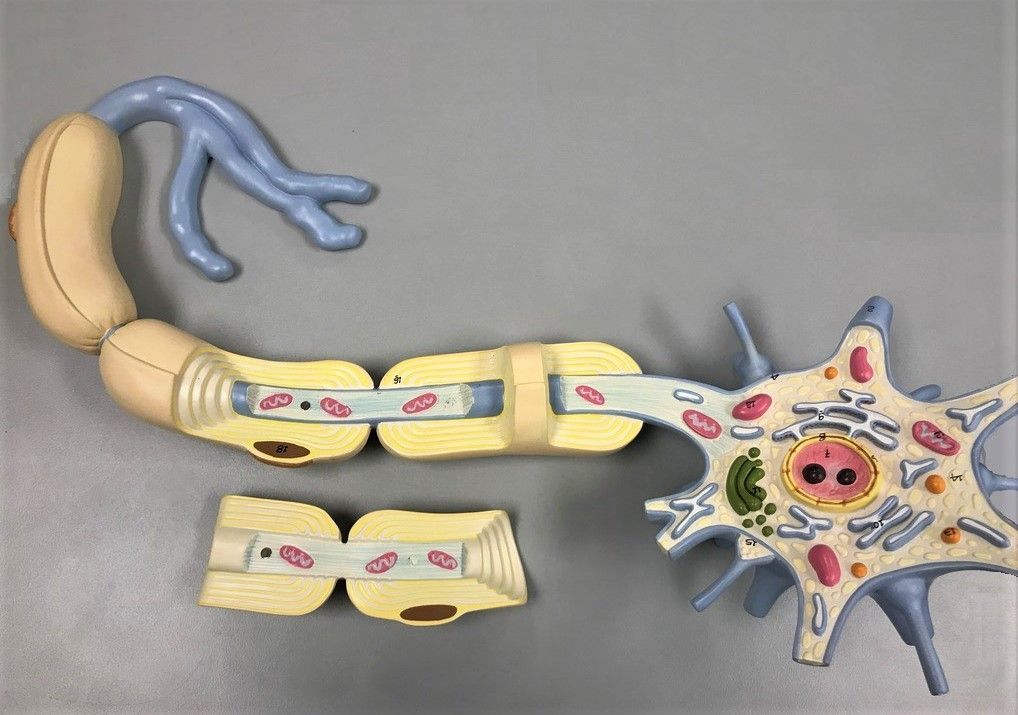
Guillain-Barre Syndrome (GBS) is a rare neurological disorder that affects the peripheral nerves, causing muscle weakness and paralysis. The exact cause of GBS is still unknown, but it is often preceded by an infection, such as a respiratory or gastrointestinal infection. The immune system, in an attempt to fight off the infection, mistakenly attacks the nerves, leading to the symptoms of GBS.
The symptoms of GBS can vary from mild to severe and can progress rapidly. Common symptoms include muscle weakness, tingling or numbness in the extremities, difficulty walking or moving, and in severe cases, paralysis. GBS can also affect the muscles responsible for breathing and swallowing, which can be life-threatening.
The impact of GBS on individuals and their families is significant. The sudden onset of symptoms and the potential for long-term disability can be overwhelming. GBS can disrupt every aspect of a person's life, from their ability to work and participate in daily activities to their emotional well-being.
It is not only the individual affected by GBS who experiences the impact but also their loved ones who provide support and care.
The impact of GBS on individuals and their families
Guillain-Barre Syndrome can have a profound impact on the lives of individuals and their families. The sudden onset of symptoms such as muscle weakness, tingling sensations, and difficulty breathing can be terrifying and life-altering. GBS can lead to complete paralysis, requiring patients to rely on ventilators and other medical interventions to survive.
Not only does GBS cause physical challenges, but it can also have emotional and psychological effects. The uncertainty of the disease progression and the potential for long-term disability can create immense stress and anxiety for patients and their loved ones. The financial burden of medical treatments and ongoing care further compounds the challenges faced by individuals with GBS.
Despite these difficulties, the resilience and determination shown by GBS patients and their families are remarkable. They strive to maintain hope and seek out the best available treatments and support systems. With the promising advances in GBS research, there is now a glimmer of hope for a brighter future.
Current treatment options for GBS
Currently, treatment for Guillain-Barre Syndrome primarily focuses on managing symptoms, providing supportive care, and speeding up recovery. The most common approach involves intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) therapy, where high doses of immunoglobulins are infused into the patient's bloodstream. This treatment helps to suppress the immune system's attack on the nerves and reduce the severity of symptoms.
Another treatment option is plasmapheresis, also known as plasma exchange. This procedure involves removing the patient's plasma, which contains the harmful antibodies, and replacing it with donor plasma or a substitute. By removing the antibodies responsible for attacking the nerves, plasmapheresis aims to halt the progression of GBS and promote faster recovery.
While these treatments can be effective in many cases, they are not without limitations.
Some patients may not respond adequately to IVIG or plasmapheresis, requiring alternative approaches.
(Contact our clinic for information on specialized, one-of-a-kind equipment to treat GBS)
Additionally, these treatments primarily target the immune response and do not address the underlying cause of GBS.
This is where the promise of new therapies and clinical trials comes into play.
Promising therapies and clinical trials for GBS
The search for a cure for Guillain-Barre Syndrome has led to the development of several promising therapies and ongoing clinical trials. One such therapy is the use of monoclonal antibodies that specifically target the immune cells responsible for attacking the nerves. By blocking these cells' activity, researchers hope to prevent the destruction of nerve cells and promote healing.
Another innovative approach being explored is the use of gene therapy to modify the patient's immune cells. This involves introducing specific genetic material into the patient's cells to enhance their ability to recognize and eliminate the harmful antibodies. Although still in the early stages of research, gene therapy holds great potential for providing long-lasting relief for GBS patients.
Furthermore, advancements in immunotherapies, such as immune checkpoint inhibitors, are being investigated for their potential in treating GBS. These drugs work by enhancing the immune system's ability to recognize and attack cancer cells but may also have applications in autoimmune disorders like GBS.
Clinical trials are currently underway to assess their safety and effectiveness in GBS patients.
The role of stem cells in GBS treatment
Stem cell therapy has emerged as a promising avenue in the search for a cure for Guillain-Barre Syndrome.
Stem cells, with their unique ability to differentiate into various cell types, hold the potential to regenerate damaged nerves and promote tissue repair. Researchers are exploring different sources of stem cells, such as bone marrow and umbilical cord blood, to develop personalized treatments for GBS patients.
In preclinical studies, stem cell transplantation has shown promising results in promoting nerve regeneration and functional recovery in animal models of GBS. The transplantation of stem cells into GBS patients could potentially accelerate the healing process and improve long-term outcomes. However, further research and clinical trials are needed to establish the safety and efficacy of stem cell therapy in humans.
Alternative and complementary treatments for GBS
In addition to conventional medical treatments, many individuals with Guillain-Barre Syndrome explore alternative and complementary therapies to manage their symptoms and support their recovery. These therapies include acupuncture, yoga, meditation, and herbal supplements, among others. While the evidence for their effectiveness in treating GBS is limited, some patients report experiencing relief and improved well-being through these approaches.
It is essential for individuals considering alternative treatments to consult with their healthcare providers and ensure they do not interfere with the prescribed medical treatments.
Integrating complementary therapies into a comprehensive treatment plan may offer additional support and enhance the overall well-being of GBS patients.
Support and resources for individuals with GBS
Living with Guillain-Barre Syndrome can be challenging, but there are numerous support networks and resources available to individuals and their families. Patient advocacy organizations, such as the Guillain-Barre Syndrome Foundation International, provide valuable information, support, and resources for GBS patients and their loved ones.
Support groups and online communities offer a platform for connecting with others who share similar experiences and can provide empathy, advice, and encouragement. These networks can be instrumental in navigating the challenges of living with GBS and finding hope in shared stories of recovery and resilience.
Advocacy efforts and organizations for GBS awareness
Raising awareness about Guillain-Barre Syndrome is crucial for advancing research, improving diagnosis and treatment options, and supporting individuals affected by the condition. Various advocacy organizations and foundations are dedicated to increasing public awareness of GBS and advocating for better healthcare policies and resources.
Through educational campaigns, fundraising initiatives, and lobbying efforts, these organizations strive to make a difference in the lives of GBS patients and their families. By supporting their mission and spreading awareness, we can contribute to the ongoing efforts to find a cure and improve the quality of life for those affected by GBS.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the search for a cure for Guillain-Barre Syndrome is an ongoing journey filled with promise and hope.
Recent advancements in research and innovative therapies are bringing renewed optimism to patients and their families. From exploring the potential of stem cells to developing targeted immunotherapies, these breakthroughs offer the possibility of improved treatment outcomes and enhanced quality of life for GBS patients.
As we continue to unravel the complexities of this debilitating condition, it is essential to support individuals with GBS, raise awareness, and advocate for further research and resources. By coming together as a community, we can bring hope and healing to those affected by Guillain-Barre Syndrome and work towards a future where a cure is within reach.
Dr. Richard T Dombroski has been working with Guillain-Barre Syndrome patients at his clinic in Fort Worth, Texas. He has specialized equipment you will not find anywhere else that has proven to reduce the physical limitations GBS has put on his patients.
Many people with GBS come form all over the United States to use his therapy machines and specialized knowledge of this debilitating disease. Some of his patients are seen in the photo above.
If you, or someone you know has been diagnosed with Guillian-Barre Syndrome and have not responded well to current treatments give his office a call at 817-367-9289.
Relief and recovery could be just around the corner!
For more information on Guillain-Barre Syndrome, treatment options, and support networks, please visit the Guillain-Barre Syndrome Foundation International's website at (www.gbs-cidp.org).